COPD: Understanding, Causes, and Management Strategies
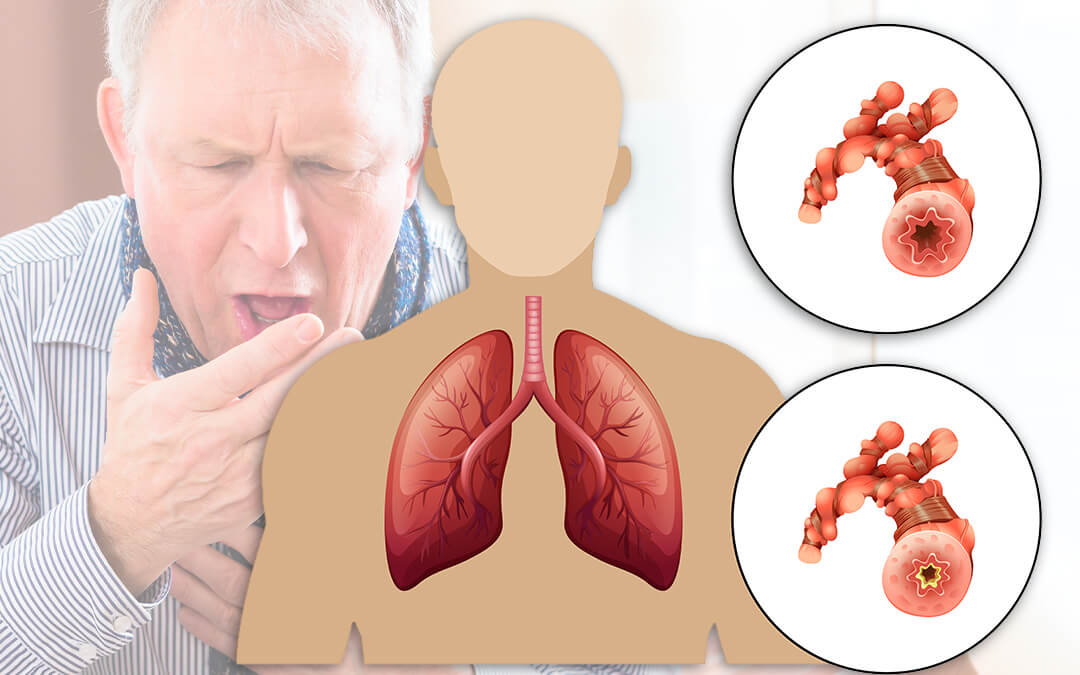
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung condition that affects breathing and overall quality of life. Early diagnosis and effective management can help individuals lead healthier lives.
Common Types of COPD
1. Chronic Bronchitis
- Cause: Long-term irritation of the airways due to smoking or pollutants.
- Symptoms: Persistent cough with mucus, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
- Treatment: Medications, pulmonary rehabilitation, and lifestyle changes.
2. Emphysema
- Cause: Damage to the air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs, often due to smoking.
- Symptoms: Breathlessness, fatigue, and reduced exercise capacity.
- Treatment: Inhalers, oxygen therapy, and breathing exercises.
3. Asthma-COPD Overlap Syndrome (ACOS)
- Cause: A combination of asthma and COPD features.
- Symptoms: Frequent coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
- Treatment: A tailored plan involving medications and lifestyle adjustments.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Smoking: The leading cause of COPD worldwide.
- Environmental Exposure: Long-term exposure to pollutants, chemicals, and dust.
- Genetics: Conditions like alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency increase the risk.
- Respiratory Infections: Frequent infections during childhood may contribute.
Prevention Tips
Avoid Smoking
- Quit smoking to reduce lung damage and improve breathing.
- Avoid secondhand smoke and smoking areas.
Protect Your Lungs
- Wear masks in polluted or dusty environments.
- Improve indoor air quality with ventilation and air purifiers.
- Stay vaccinated to prevent respiratory infections like flu and pneumonia.
Treatment Options
- Medications: Bronchodilators and corticosteroids to open airways and reduce inflammation.
- Oxygen Therapy: For severe cases to improve oxygen levels in the blood.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: Exercise programs and education to enhance lung function and quality of life.
- Surgery: Lung volume reduction or transplantation in advanced cases.
Complications of Untreated COPD
- Frequent Infections: Increased vulnerability to respiratory infections.
- Heart Problems: Higher risk of heart disease and high blood pressure in lung arteries.
- Lung Cancer: COPD patients are at a greater risk of developing lung cancer.
- Reduced Quality of Life: Severe breathlessness can limit daily activities.
Role of Healthcare Facilities
- Accurate Diagnosis: Lung function tests like spirometry to confirm COPD.
- Comprehensive Care: Multidisciplinary teams providing medical and lifestyle support.
- Emergency Services: Immediate care for COPD exacerbations.
- Follow-Up Support: Regular monitoring to prevent complications.
Conclusion
COPD is a manageable condition with the right approach. By avoiding risk factors, seeking timely medical care, and adopting healthier habits, individuals with COPD can improve their quality of life. Take proactive steps to breathe easier and live better!