Asthma: Understanding, Management, and Prevention
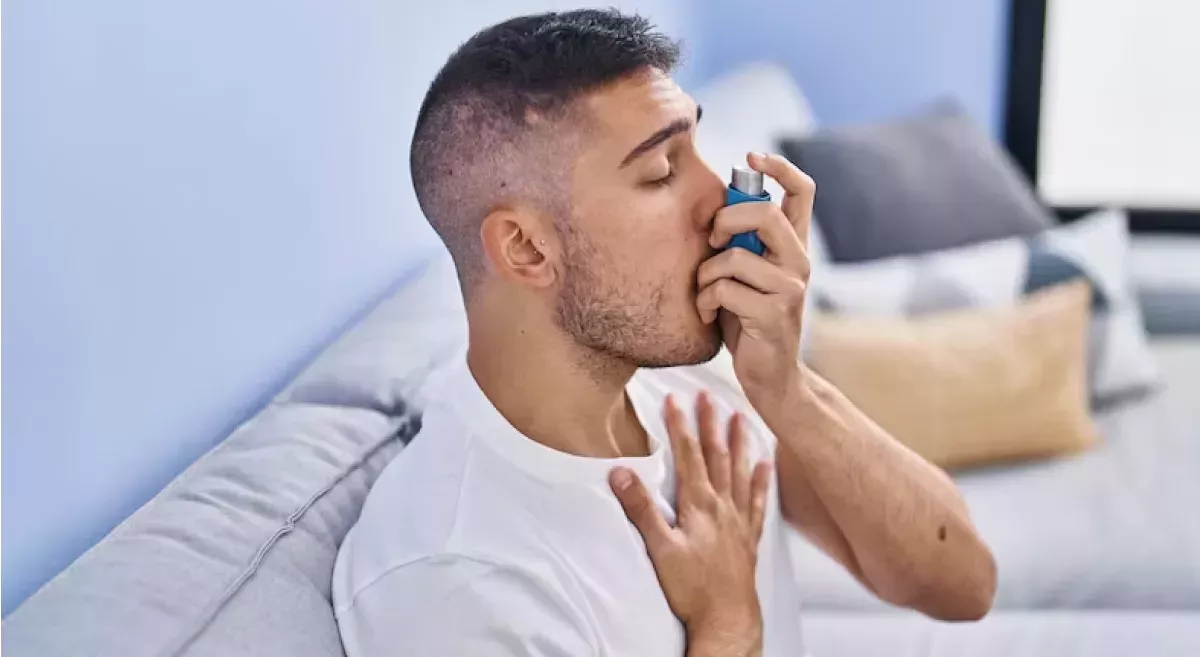
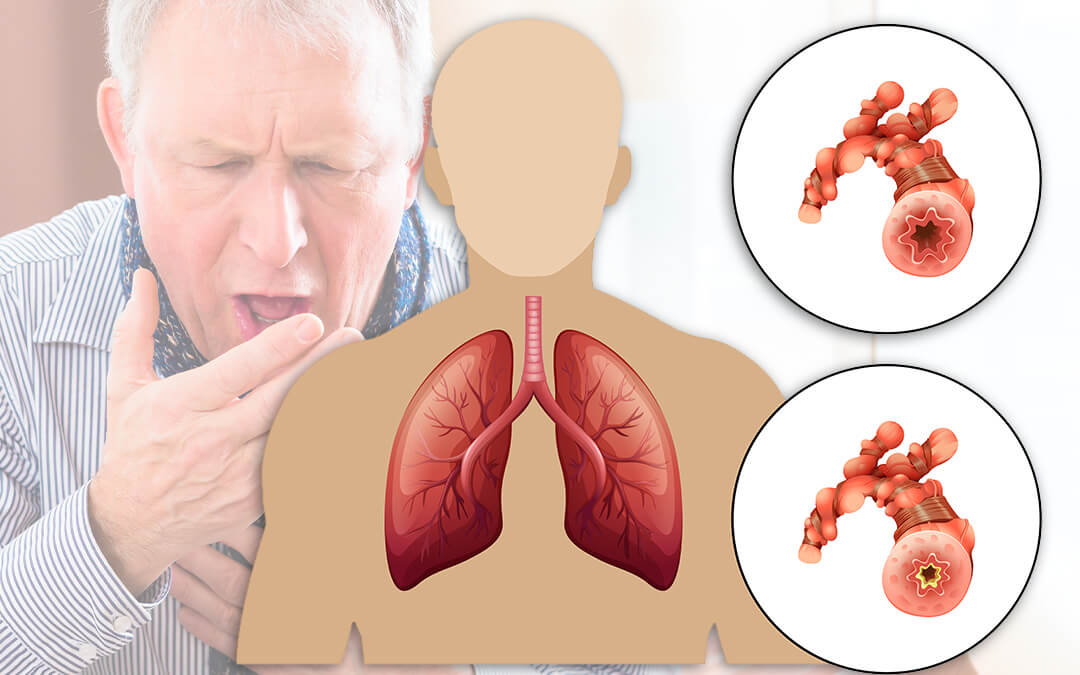
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to difficulty breathing. Proper management and preventive measures can help individuals lead a healthy life despite the condition.
Types of Asthma
1. Allergic Asthma
- Cause: Triggered by allergens like pollen, dust mites, or pet dander.
- Symptoms: Wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness.
- Management: Avoid allergens and use prescribed medications like inhalers.
2. Exercise-Induced Asthma
- Cause: Triggered by physical activity, especially in cold or dry air.
- Symptoms: Shortness of breath, chest pain, and fatigue during exercise.
- Management: Warm up before exercise and use preventative inhalers.
3. Occupational Asthma
- Cause: Exposure to irritants like chemicals, dust, or fumes in the workplace.
- Symptoms: Persistent coughing, wheezing, and chest tightness at work.
- Management: Implement workplace safety measures and consult a specialist.
4. Nocturnal Asthma
- Cause: Symptoms worsen at night due to triggers like dust mites or reflux.
- Symptoms: Nighttime coughing, wheezing, and disrupted sleep.
- Management: Optimize bedroom environment and follow prescribed treatments.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Genetics: Family history of asthma or allergies.
- Environmental Triggers: Pollution, smoke, and allergens.
- Respiratory Infections: Early-life infections can increase asthma risk.
- Obesity: Linked to increased severity of asthma symptoms.
Prevention Tips
Avoid Triggers
- Keep your living space free of dust and allergens.
- Avoid smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke.
- Wear masks in high-pollution or allergen-heavy areas.
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
- Follow a balanced diet to reduce inflammation.
- Engage in regular exercise tailored to your condition.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation.
Treatment and Management
- Medications: Inhaled corticosteroids, bronchodilators, and leukotriene modifiers to control symptoms.
- Action Plan: Work with a healthcare provider to create a personalized asthma action plan.
- Allergy Management: Treat underlying allergies to reduce asthma flare-ups.
- Regular Monitoring: Use peak flow meters to track lung function.
Complications of Untreated Asthma
- Frequent Hospitalizations: Severe attacks may require emergency care.
- Lung Damage: Chronic inflammation can lead to long-term damage.
- Impaired Daily Activities: Symptoms can limit physical and social activities.
- Reduced Quality of Life: Persistent symptoms can cause emotional and physical stress.
Role of Healthcare Facilities
- Comprehensive Diagnosis: Lung function tests and allergy assessments for accurate diagnosis.
- Specialist Care: Pulmonologists and allergists for tailored treatment plans.
- Emergency Support: Access to care during severe asthma attacks.
- Patient Education: Guidance on medication use and lifestyle adjustments.
Conclusion
Asthma, while chronic, is manageable with the right strategies and medical support. By identifying triggers, following a personalized treatment plan, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, individuals with asthma can lead fulfilling lives. Take proactive steps to breathe easier and live better today!