Diabetes: Understanding, Management, and Prevention
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels. Proper management and awareness are crucial for living a healthy life with diabetes.
Types of Diabetes
1. Type 1 Diabetes
- Cause: An autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
- Symptoms: Increased thirst, frequent urination, extreme hunger, and weight loss.
- Management: Requires daily insulin injections and blood sugar monitoring.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
- Cause: Insulin resistance combined with insufficient insulin production.
- Symptoms: Fatigue, blurred vision, slow-healing wounds, and frequent infections.
- Management: Lifestyle changes, oral medications, and, in some cases, insulin therapy.
3. Gestational Diabetes
- Cause: Develops during pregnancy due to hormonal changes affecting insulin sensitivity.
- Symptoms: Often asymptomatic; diagnosed through routine blood sugar screening during pregnancy.
- Management: Controlled through diet, exercise, and occasionally insulin.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Genetic Factors: A family history of diabetes increases risk.
- Obesity: Excess weight contributes to insulin resistance.
- Inactive Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity reduces insulin efficiency.
- Unhealthy Diet: High sugar and processed food intake elevate blood sugar levels.
Prevention Tips
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking, cycling, or swimming.
- Avoid excessive sugar and processed foods.
Regular Health Monitoring
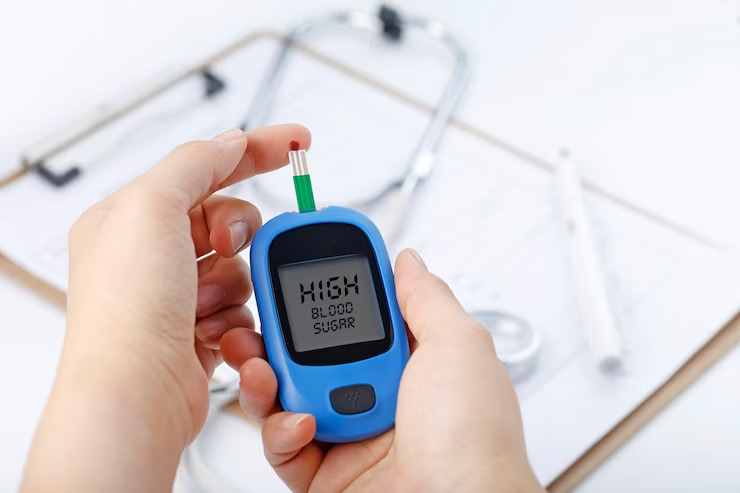
- Check blood sugar levels regularly, especially if you are at risk.
- Monitor body weight to stay within a healthy range.
- Undergo routine medical check-ups for early detection.
Treatment and Management
- Medications: Insulin therapy for Type 1 and oral medications or insulin for Type 2.
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regularly checking glucose levels helps maintain control.
- Healthy Eating Plans: Following a diabetes-specific diet prescribed by a nutritionist.
- Exercise: Improves insulin sensitivity and helps manage weight.
- Stress Management: Reduces the impact of stress on blood sugar levels.
Complications of Untreated Diabetes
- Heart Disease: Increased risk of cardiovascular conditions like heart attacks and strokes.
- Kidney Damage: Diabetes can lead to kidney failure if not managed properly.
- Nerve Damage: Prolonged high blood sugar can damage nerves, causing pain or loss of sensation.
- Eye Conditions: Risk of blindness due to diabetic retinopathy.
- Foot Problems: Poor circulation and nerve damage can lead to serious foot infections.
Role of Healthcare Facilities
- Diabetes Clinics: Specialized care for managing and treating diabetes.
- Health Education: Providing information on lifestyle changes and treatment options.
- Support Groups: Offering emotional support and shared experiences.
- Advanced Treatments: Access to technologies like continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and insulin pumps.
Conclusion
While diabetes is a lifelong condition, it can be effectively managed with the right approach. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, monitoring blood sugar levels, and seeking timely medical advice, individuals can lead a fulfilling life despite diabetes. Take charge of your health today to prevent complications tomorrow.