Seasonal Diseases: Understanding, Prevention, and Treatment
Seasonal diseases are illnesses that become more prevalent during specific times of the year, typically influenced by environmental changes such as temperature, humidity, and rainfall. Understanding these diseases and taking preventive measures can significantly reduce their impact.
Common Seasonal Diseases
1. Summer-Related Diseases
- Heatstroke: Caused by prolonged exposure to high temperatures. Symptoms include dizziness, fainting, and confusion.
- Dehydration: Leads to fatigue, weakness, and electrolyte imbalances due to excessive sweating.
- Foodborne Illnesses: Spoiled food in hot weather can cause diarrhea and food poisoning.
- Skin Diseases: Conditions such as sunburn, rashes, and fungal infections are common in summer.
2. Monsoon-Related Diseases
- Dengue and Malaria: Spread by mosquitoes breeding in stagnant water.
- Cholera and Typhoid: Result from consuming contaminated water and poor sanitation.
- Leptospirosis: Caused by wading through flooded areas.
- Fungal Infections: Humidity and dampness lead to skin infections.
3. Winter-Related Diseases
- Common Cold and Flu: Viral infections spread easily during cold weather.
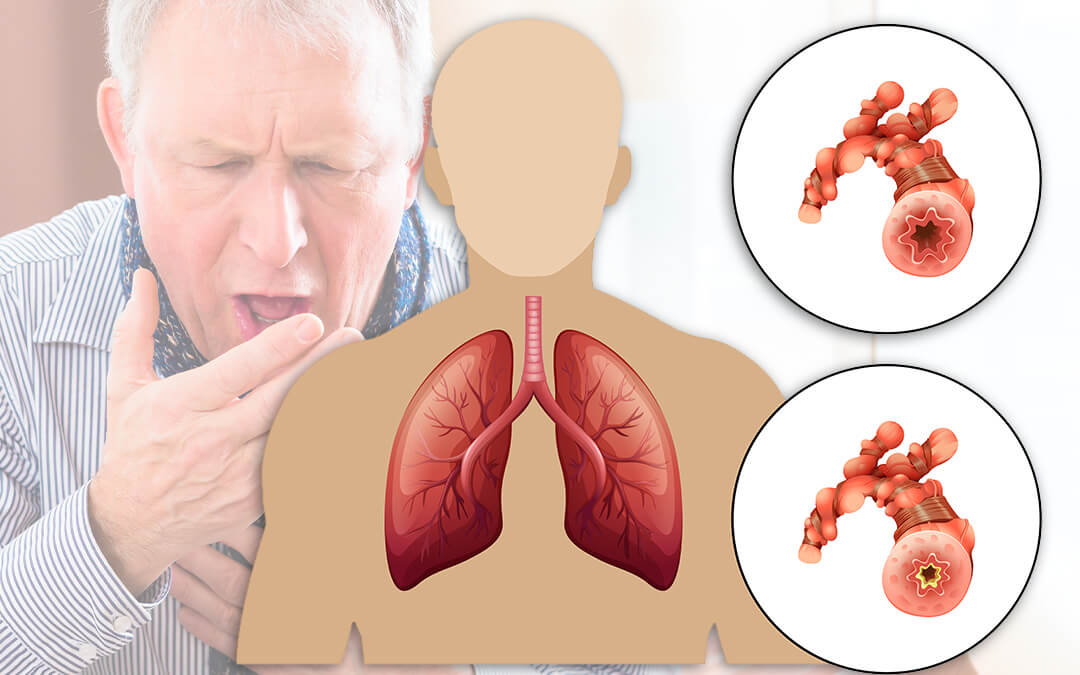
- Pneumonia and Bronchitis: Respiratory infections worsen in winter, especially in vulnerable individuals.
- Asthma Attacks: Cold air can exacerbate asthma symptoms.
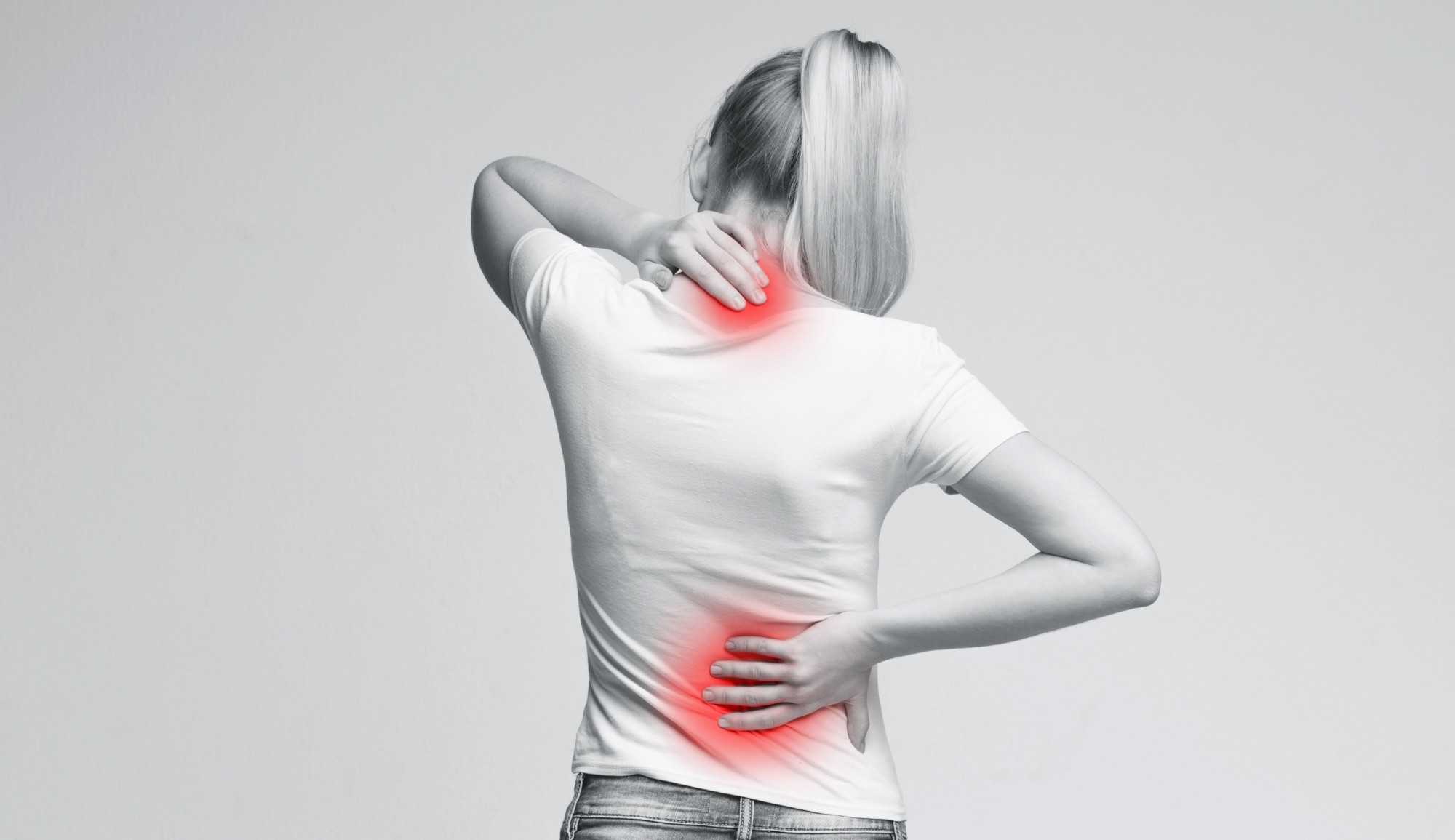
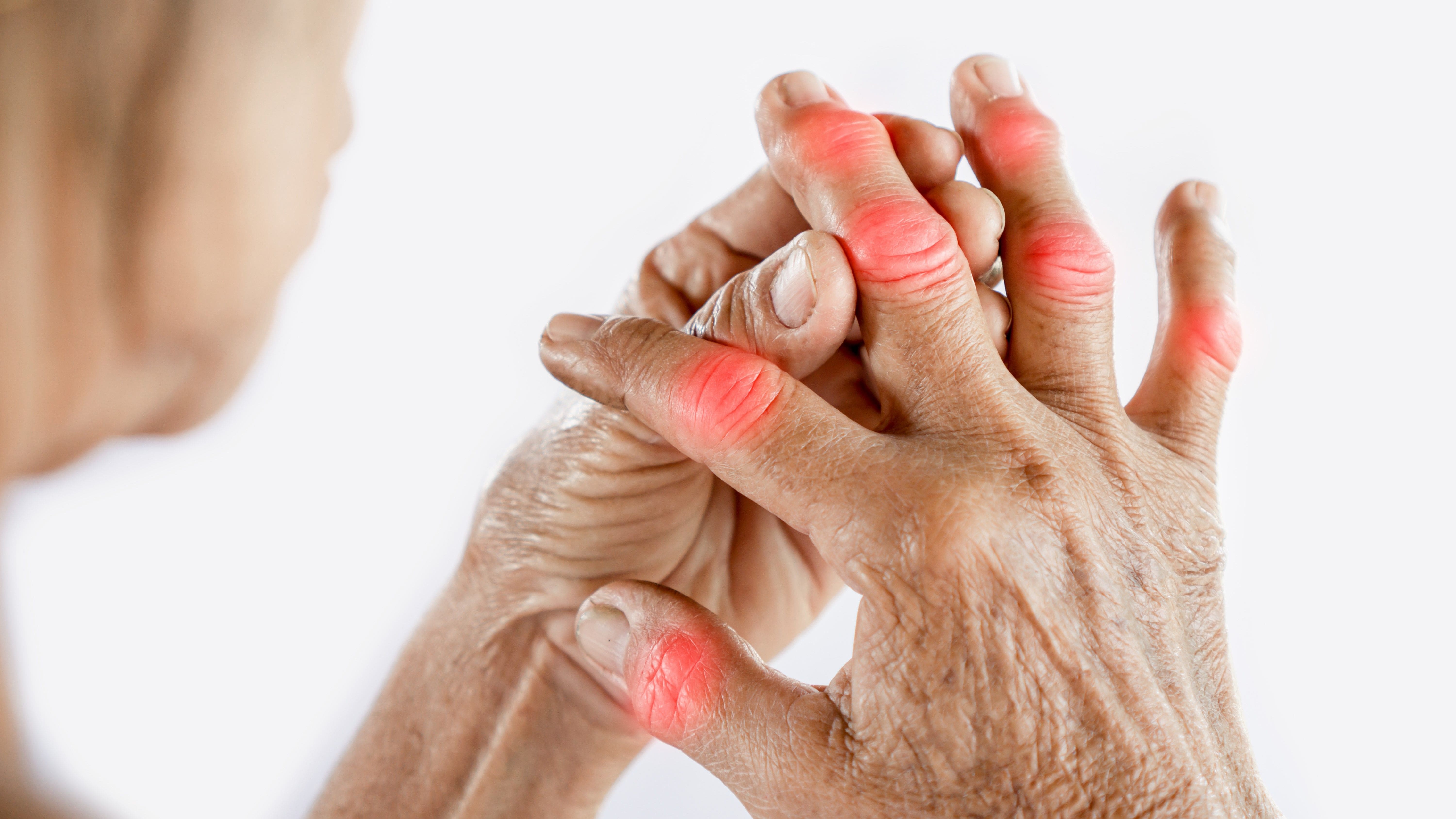
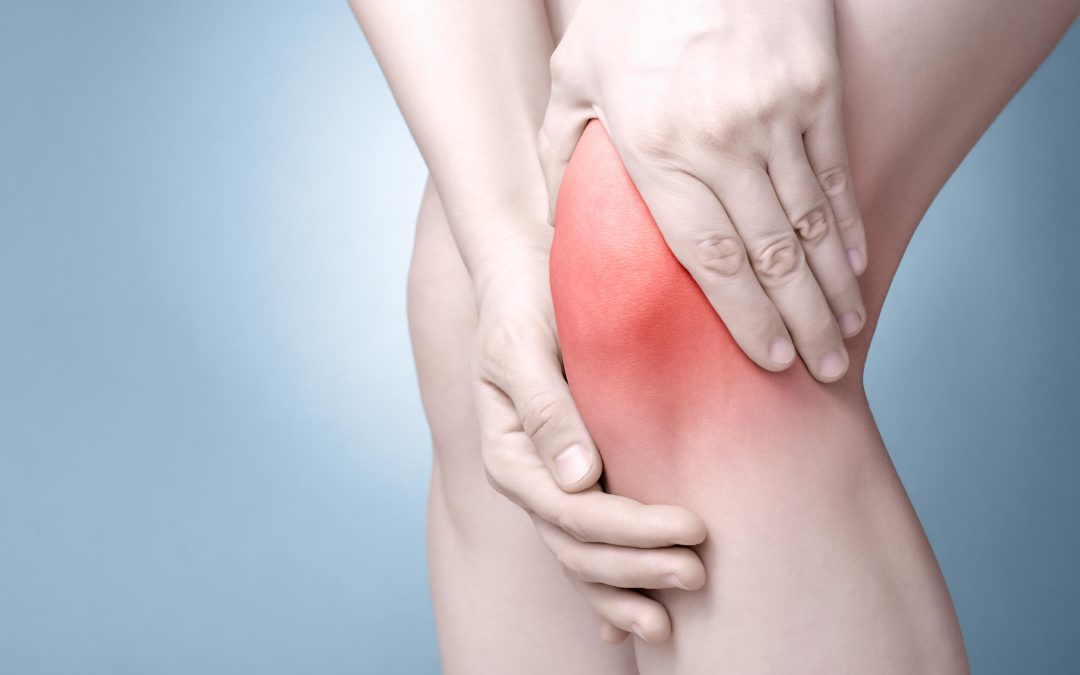
- Joint Pain: Arthritis-related pain increases during colder months.
4. Spring and Fall Allergies
- Hay Fever: Triggered by pollen, causing sneezing and itchy eyes.
- Asthma: Seasonal changes can worsen asthma symptoms.
- Skin Allergies: Allergens like pollen and mold can cause rashes.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Environmental Factors: Seasonal changes influence pathogen survival and transmission.
- Poor Hygiene and Sanitation: Contaminated water and food contribute to the spread of diseases.
- Weakened Immunity: The immune system is stressed during seasonal changes.
- Insect Breeding: Mosquitoes thrive in stagnant water during the monsoon.
Prevention Tips
General Hygiene Practices
- Wash hands frequently with soap and water.
- Use hand sanitizers when soap and water are unavailable.
- Avoid sharing personal items like towels and utensils.
Seasonal-Specific Measures
- Summer: Stay hydrated, use sunscreen, and wear light clothing.
- Monsoon: Prevent water stagnation, use mosquito repellents, and drink purified water.
- Winter: Dress warmly, use humidifiers, and maintain a balanced diet.
- Spring/Fall: Limit outdoor activities during peak pollen hours and use air purifiers indoors.
Treatment and Management
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Manage colds and mild allergies with OTC options.
- Medical Consultation: Seek professional advice for persistent or severe symptoms.
- Hydration Therapy: Rehydrate with ORS for conditions like diarrhea.
- Antibiotics/Antivirals: For bacterial infections such as typhoid or pneumonia.
- Immunizations: Vaccines help protect against preventable diseases.
Role of Healthcare Facilities
- Awareness Campaigns: Educating the public on prevention and symptoms.
- Vaccination Drives: Providing immunizations for flu and pneumonia.
- Timely Diagnosis: Advanced tools for early disease detection.
- Specialist Care: Access to experts for effective treatment.
Conclusion
Seasonal diseases are inevitable, but their impact can be minimized through awareness, preventive care, and timely treatment. By adopting simple hygiene practices, making lifestyle adjustments, and seeking medical advice when needed, you can protect yourself and your loved ones throughout the year. Prioritize your health and stay informed to enjoy a disease-free year!