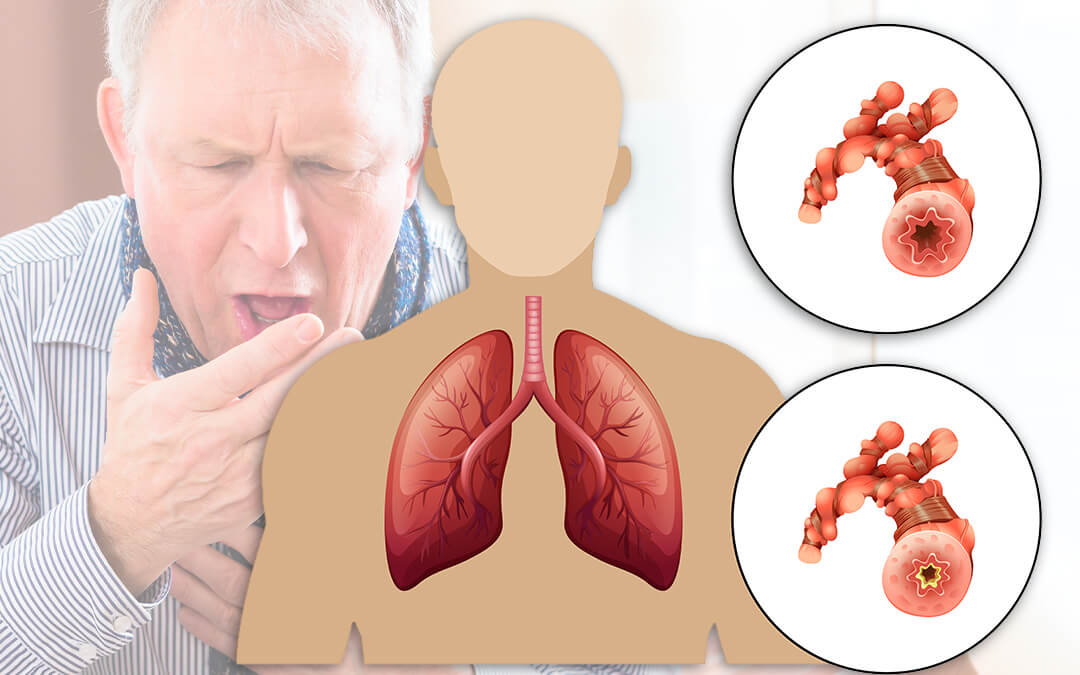
Breathing-Related Problems: Understanding, Management, and Prevention
Breathing-related problems encompass a variety of conditions that affect the respiratory system, making it difficult for individuals to breathe normally. Understanding these conditions and adopting preventive measures can greatly enhance quality of life.
Types of Breathing-Related Problems
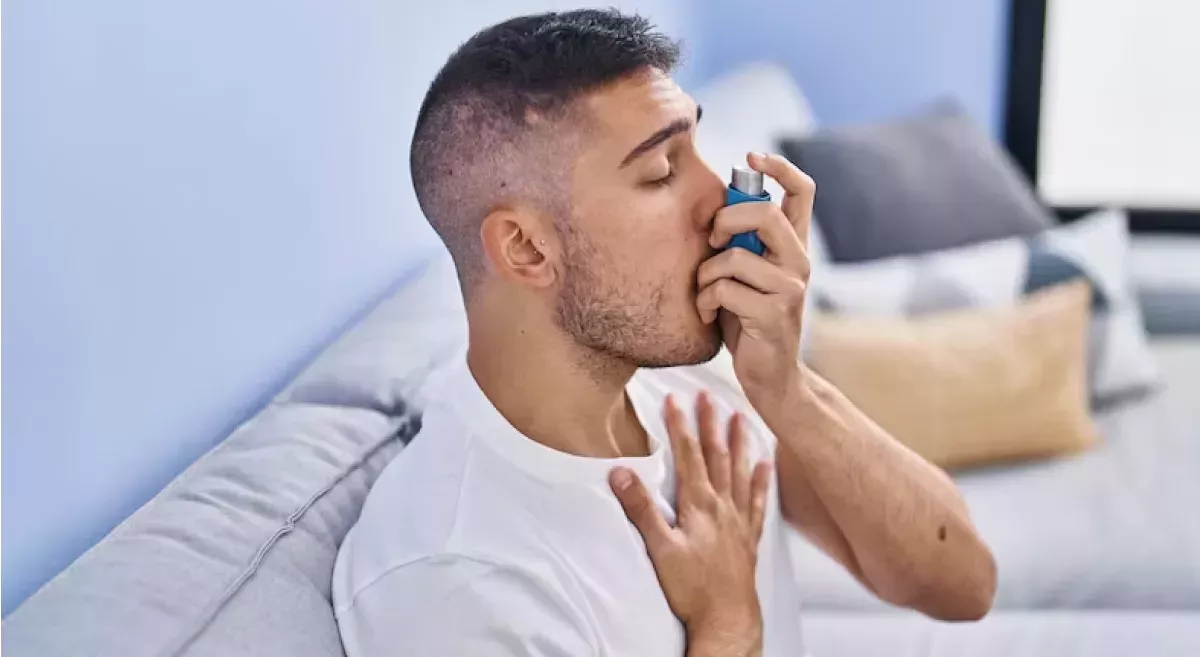
1. Asthma
- Cause: Chronic inflammation of the airways, triggered by allergens, exercise, or pollution.
- Symptoms: Wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing.
- Management: Use of inhalers, avoiding triggers, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
2. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Cause: Long-term exposure to irritants such as cigarette smoke or air pollution.
- Symptoms: Chronic cough, frequent respiratory infections, and difficulty breathing.
- Management: Medications, oxygen therapy, and pulmonary rehabilitation.
3. Allergic Rhinitis
- Cause: Allergic reaction to pollen, dust, or animal dander.
- Symptoms: Nasal congestion, sneezing, and itchy eyes.
- Management: Antihistamines, nasal sprays, and reducing allergen exposure.
4. Respiratory Infections
- Cause: Viral or bacterial infections affecting the lungs, such as pneumonia or bronchitis.
- Symptoms: Fever, persistent cough, and difficulty breathing.
- Management: Antibiotics for bacterial infections, rest, and hydration.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Smoking: Major cause of COPD and lung cancer.
- Pollution: Exposure to air pollutants aggravates respiratory conditions.
- Allergens: Dust, pollen, and mold trigger allergic reactions and asthma attacks.
- Infections: Frequent respiratory infections can weaken the lungs.
Prevention Tips
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- Avoid smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke.
- Maintain a balanced diet to strengthen the immune system.
- Engage in regular exercise to improve lung capacity.
Environmental Measures
- Use air purifiers to reduce indoor pollution.
- Wear masks in high-pollution areas or during allergy seasons.
- Keep living spaces clean and free of dust and mold.
Treatment and Management
- Medications: Inhalers, bronchodilators, and antihistamines for symptom relief.
- Oxygen Therapy: For individuals with severe respiratory conditions like COPD.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: A program of exercise and education to manage chronic conditions.
- Vaccinations: Flu and pneumonia vaccines to prevent respiratory infections.
- Hydration: Helps thin mucus for easier breathing.
Complications of Untreated Breathing Problems
- Respiratory Failure: Severe cases may require mechanical ventilation.
- Heart Strain: Chronic lung conditions can lead to heart complications.
- Reduced Quality of Life: Limited physical activity and frequent hospitalizations.
- Increased Infections: Weakened lungs are more prone to infections.
Role of Healthcare Facilities
- Specialist Clinics: Provide care for chronic respiratory conditions.
- Diagnostic Tools: Spirometry and imaging tests for accurate diagnosis.
- Rehabilitation Programs: Help patients manage symptoms and regain independence.
- Education Campaigns: Spread awareness about prevention and early detection.
Conclusion
Breathing-related problems can significantly impact daily life but can be effectively managed with early detection and proper care. By adopting healthy habits, avoiding triggers, and seeking medical advice when necessary, you can breathe easier and live better. Take proactive steps to protect your respiratory health today!